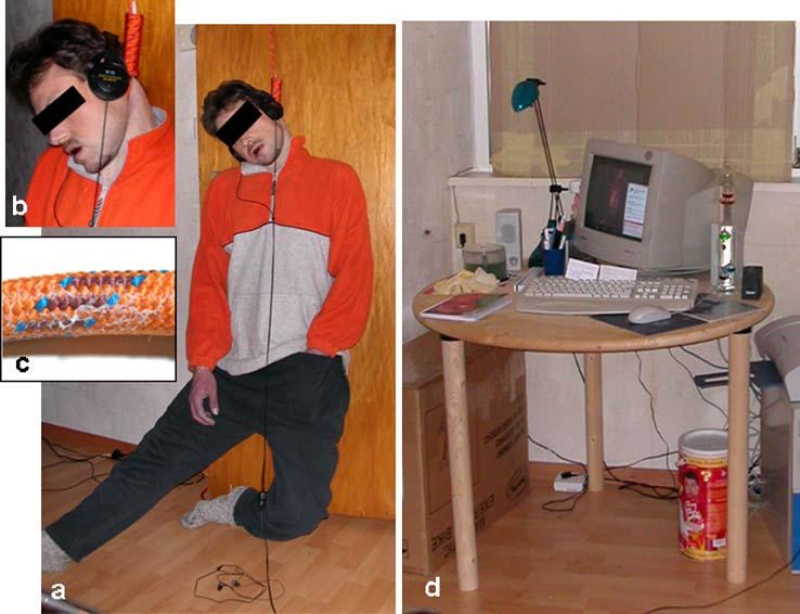
The body of a 30-year-old man was found hanged in the living room of his flat on the ground floor. A neighbour had informed the police after seeing the body through the window from outside. The body was dressed with an orange- gray pullover, dark cotton tracksuit pants and a pair of socks. There were no underpants.
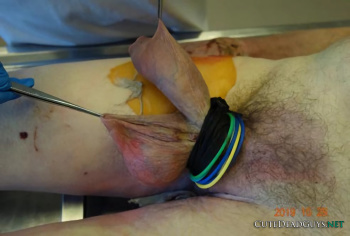
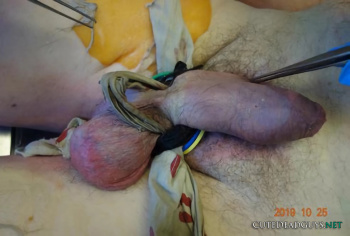
Both legs of the victim were touching the floor with the right leg being extended and the left leg bent at the knee joint more or less at a right angle. The left hand was inside the waistband of the trousers close to the genital region.
The tool used for strangulation was a thick plaited plastic rope (approximately 1 cm in diameter) which formed a slip-knot deeply impressed into the anterior and lateral soft tissue parts of the neck. The knot was at the highest point of the hanging mark on the left side of the nape of the neck behind the left ear. The noose was not padded against the skin of the neck. The other end of the rope had been passed over the upper edge of the door and fastened to the handle on the other side. The deceased was wearing headphones connected to the computer which was running and in full view of the victim. The screen showed the picture of an allegedly hanged female (the last section of a so-called snuff video).
At the forensic autopsy, the following findings were documented.
Hypostasis was no longer displaceable, and the localization was consistent with a hanging position of the body after death. A 1.5-cm-wide strangulation mark was present rising on both sides of the neck with the highest point being localized at the nape of the neck behind the left ear. On the ligature, peeled off epidermal flakes were found.
Hemorrhages caused by strain on the points of attachment of both mm. sternocleidomastoidei were present as a sign of vital hanging.
The skin above the hanging mark and the mucous membranes of the face were pale and free of petechial hemorrhages. The tongue was behind the teeth, and the tissue of the tongue did not show any blood extravasation.
Moreover, advanced sarcoidosis with numerous grayishwhite nodules up to 5 mm in size was found in both lungs, especially the upper lobes, as well as the liver and the spleen. In the thorax and the abdomen, further lymph node conglomerates sized up to 5 cm could be demonstrated.
Histologically, there were characteristic epithelioid cell granulomas without central caseation containing numerous Langhans’ giant cells with typical nuclei arranged in an arciform manner.
The alcohol concentration was 0.21 g/l in femoral venous blood and 0.35 g/l in urine.